Creating Buttons and Plugins¶
Creating Button Toolbar Models¶
Button toolbar models are a special kind of model in the sense that they can be loaded as models and as toolbars. Example button models are provided under Toolbars.
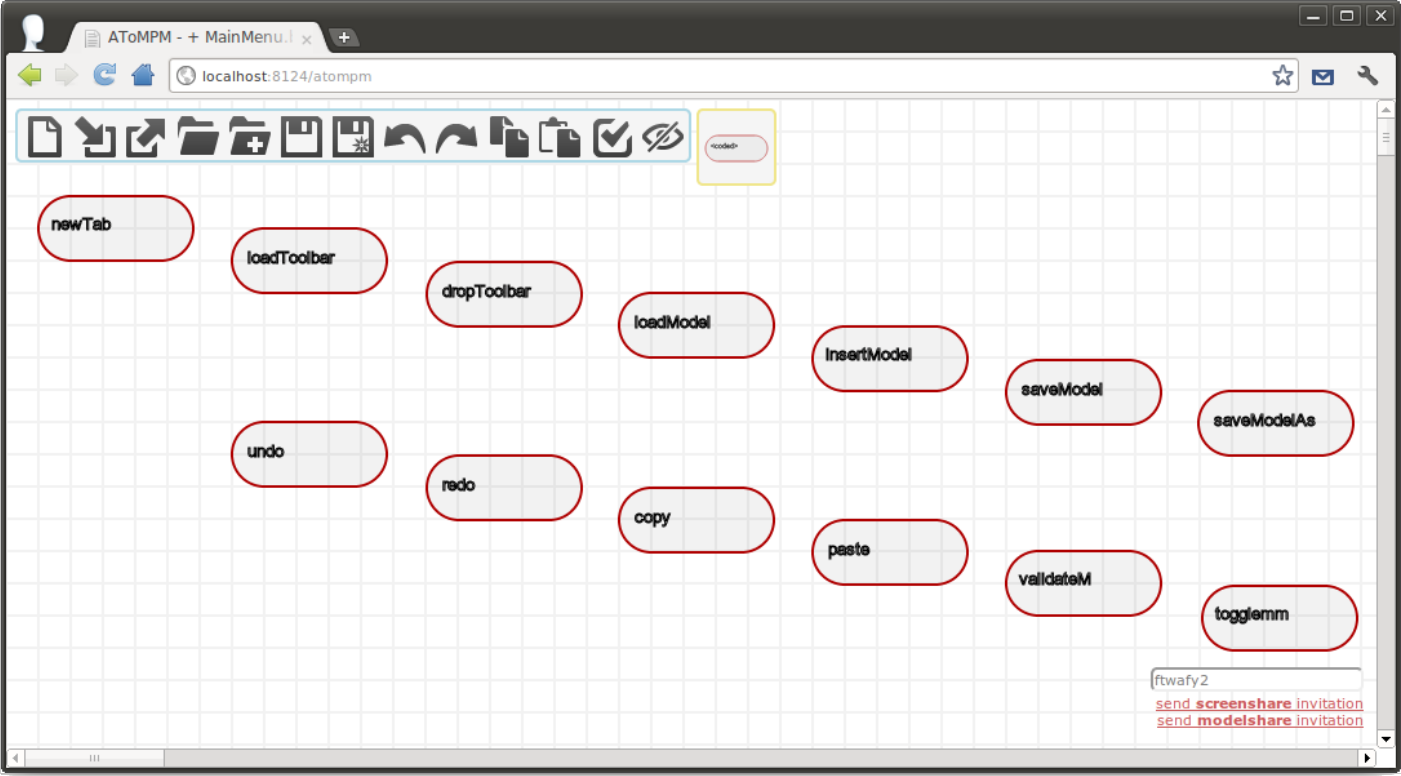
The figure above shows the model that defines the MainMenu button toolbar. Each entity of the Button type has three attributes: name, tooltip and code.
name is displayed in concrete syntax and is used to resolve the file name of the button’s associated toolbar icon: given name N, there should be an icon named n.icon.png in the same folder as the model.
tooltip becomes the icon’s tooltip, i.e., hovering the mouse cursor over a button’s toolbar icon displays the value of its tooltip attribute.
code is a code snippet that is evaluated when the toolbar icon is clicked. This code must be valid JavaScript and can make use of the AToMPM Client API, detailed in the following Subsection.
Finally, the layout of Button entities dictates their order in the toolbar: higher and leftmost buttons are shown first.
Plugins¶
Plugin files are written in Javascript and placed in the plugins/ folder. These plguins functions or classes can then be accessed by button or transformation code within AToMPM.
Client API¶
The following functions can be accessed from within the code attribute of Button entities in button toolbar models and from the Console.
Note that several button toolbar models which make exhaustive use of these functions are provided under /Toolbars/.
- function _compileToASMM(fname)
Compile a model, specified by its full path (relative to the current user’s trunk), into an abstract syntax meta-model. An error message will be produced if the specified model is not a model of a formalism’s abstract syntax. As of now, such models may only be expressed in the bundled SimpleClassDiagram or EntityRelationship formalisms. Also, note that a recommended (but not enforced) naming convention is that models of formalism abstract syntax be named
FORMALISM_NAMEMM.model.- function _compileToCSMM(fname)
Compile a model, specified by its full path (relative to the current user’s trunk), into a concrete syntax (or icon definition) meta-model. An error message will be produced if the specified model is not a model of a formalism’s concrete syntax. As of now, such models may only be expressed in the bundled ConcreteSyntax formalism. Note that enforced naming conventions are that models of formalism concrete syntax must be named
FORMALISM_NAME.DESCRIPTIONIcons.model, and that exactly one concrete syntax definition should be namedFORMALISM_NAME.defaultIcons.model.- function _compileToPatternMM(fname)
Produce pattern abstract and concrete syntax meta-models given an abstract syntax meta-model, specified by its full path (relative to the current user’s trunk). An error message will be produced if the specified meta-model is not an abstract syntax meta-model.
- function _copy()
Copy selected entities (if any). Note that it is impossible to copy edges if any of their extremities aren’t also selected.
- function _exportSVG(fname)
Prompt the user to download an SVG image representation of the current model and save it under the given filename. When fname is omitted, target filename defaults to
model.svg.- function _getUserPreferences(callback[,subset])
Call callback with the contents of the logged in user’s preferences file (see Section Tweaking Default Settings), or a subset of it. When subset is defined, it should be an array of desired user’s preference keys.
- function _httpReq(method,url,params,onresponse[,sync])
Perform a synchronous or asynchronous HTTP request given an HTTP method (GET, PUT, POST or DELETE), a URL, a key-value dictionary of parameters, and a function that should handle the request’s response. The onresponse function should expect two parameters: statusCode and responseData.
- function _insertModel(fname)
Load a model, specified by its full path (relative to the current user’s trunk), alongside the current model.
- function _loadModel(fname)
Load a model, specified by its full path (relative to the current user’s trunk), overwriting the current model, if any.
- function _loadToolbar(fname)
(Re-)Load one or more button or formalism toolbars, specified by their full path (relative to the current user’s trunk).
- function _openDialog(type,args,callback)
Pop-up a dialog box for user interaction. Valid values for the type parameter are _CLOUD_DATA_MANAGER, _DICTIONARY_EDITOR, _ENTITY_EDITOR, _ERROR, _FILE_BROWSER, _LEGAL_CONNECTIONS, _LOADED_TOOLBARS and _CUSTOM. Each type requires its own set of arguments encoded in the args parameter. As for the callback parameter, it is a one-argument function called with the sum of the user’s input when and if the user presses OK on the dialog.
The _CLOUD_DATA_MANAGER dialog is used to manage user data stored within the user’s personal cloud space. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary with the following optional keys: extensions, readonly and title. Values for the extensions key should be arrays of regular expressions describing allowed file names. When omitted, all file names are allowed. Values for the readonly key should be booleans denoting whether or not the provided dialog should allow cloud data modifications. When omitted, modifications are allowed. Finally, the title argument is a string that denotes the dialog’s title.
The _DICTIONARY_EDITOR dialog is used to read and edit arbitrary typed dictionaries. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary of the form:
{
data : < a typed dictionary >,
ignoreKey : < a function that takes two parameters, a key and a value, and
returns true if they should be shown in the editing dialog >,
keepEverything : < a function that returns false if only updated key-value pairs
should be remembered by the editing dialog >,
title : < an optional dialog's title>
}
The _ENTITY_EDITOR dialog is used to read and edit abstract entity attributes. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary of the form:
{
uri : < some entity URI >
}
The _ERROR dialog is used to report an error (e.g., attempting to connect elements that can not be connected) to the user. Its args parameter should be a string of text describing the error.
The _FILE_BROWSER dialog is used to browse and select files stored within the user’s personal cloud space. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary with the following optional keys: extensions, multipleChoice, manualInput and title.
Values for the extensions key should be arrays of regular expressions describing allowed file names. When omitted, all file names are allowed. Values for the multipleChoice key should be booleans denoting whether or not several files can be selected simultaneously. When omitted, only one file can be selected at a time. Values for the manualInput key should be booleans denoting whether or not manual file name entry should be permitted. When omitted, manual file name entry is disabled. Finally, the title argument is a string that denotes the dialog’s title.
The _LEGAL_CONNECTIONS dialog is used to provide the user with a choice of legal connection types between entities he/she is trying to connect when more than one such connection type is available. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary of the form:
{
uri1 : < source entity URI >,
uri2 : < target entity URI >,
ctype : containment | visual,
forceCallback : true | false
}
The forceCallback argument indicates whether or not the dialog callback function should be called in the event where no legal connections are available. When unset, the default behaviour is to pop up an error.
The _LOADED_TOOLBARS dialog is used to select loaded button and formalism toolbars. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary with the following keys: multipleChoice, type and title.
Values for the multipleChoice key should be booleans denoting whether or not several toolbars can be selected simultaneously. Values for the type key should be metamodels, buttons, or undefined. Finally, the optional title argument is a string that denotes the dialog’s title.
Last but not least, the _CUSTOM dialog enables entirely user-specified dialogs. Its args parameter should be a key-value dictionary of the form:
{
widgets : [ < ..., widgetDescription_i, ... > ]
title : < an optional dialog's title>
}
where widgetDescription_i has the form:
{
id : < widgetId >,
type : input,
label : < input label >,
default : < default value in input field >
}
for input fields, and
{
id : < widgetId >,
type : select,
choices : [ < ..., < choice_i >, ... > ],
multipleChoice : true | false
}
for lists of choices.
- function _paste()
Paste copied entities (if any). Note that copied entities may originate from another AToMPM client.
- function _redo()
Redo the last undone action.
- function _saveModel([fname,backup])
Persist a model, specified by its full path (relative to the current user’s trunk), to the user’s personal cloud space. If the backup flag is set, the provided filename will not be set as the current filename, and the window title will not be altered to indicate that changes have been saved.
- function _setInvisibleMetamodels(mms)
Make all entities from the given formalisms, specified via their full paths (relative to the current user’s trunk), invisible.
- function _setUserPreferences(prefs[,callback])
Update the logged in user’s preferences file. prefs should be a key-value dictionary. Note that prefs need not contain keys and values for all existing user preference keys: missing keys will retain their current value.
- function _setTypeToCreate(fulltype)
Set the type of entities that will be created when the user creates new entities on the Canvas.
- function _spawnClient(fname,callbackURL)
Spawn a new instance of AToMPM. If a model is specified via the fname parameter, it is loaded into the new instance. If a callback url is specified via the callbackURL parameter, critical information about the new instance is POSTed to it upon its creation.
- function _spawnHeadlessClient(context,onready,onchlog)
TBC.
- function _undo()
Undo the last performed action.
- function _unloadToolbar(tb)
Close one or more of the loaded button and formalism toolbars, specified via their full paths (relative to the current user’s trunk).
- function _validate()
Verify abstract syntax validity constraints (if any) for all loaded formalisms.
Remote API¶
AToMPM also supports a limited Remote API that can be used to edit and animate models remotely, e.g., from third-party or synthesized applications. This is achieved by forwarding specially formatted HTTP queries targeted at the back-end to the client. The said queries must have the form:
method : PUT
url : < backendURL >/GET/console?wid=< aswid >
data : {text: CLIENT_BDAPI :: < func >}
where aswid is an identifier for the client’s associated back-end abstract syntax thread (retrievable by typing __aswid in the client Console), and func is a string representation of a key-value dictionary of the form:
{
func : < Remote API function name >,
args : { < ..., < arg_i : value_i >, ... > }
}
The methods accessible via the Remote API are detailed below.
function _highlight(args)
args =
{
asid : < abstract syntax entity identifier >,
followCrossFormalismLinks : undefined | * | DOWN | UP,
timeout : undefined | < timeout >
}
Highlight the given entity, specified via its abstract syntax identifier, and un-highlight any highlighted nodes. The followCrossFormalismLinks parameter indicates whether or not (and which) neighbours along cross-formalism links should also be highlighted. The timeout parameter, if specified, indicates the duration of the highlight (in milliseconds).
function _loadModelInNewWindow(args)
args =
{
fname : < model file name >,
callback-url : < callback URL >
}
function _tag(args)
args =
{
asid : < abstract syntax entity identifier >,
text : < text to display >,
style : { < ..., < key_i : value_i >, ...> },
append : true | false,
timeout : undefined | < timeout >
}
Tag the given entity, specified via its abstract syntax identifier, with appropriately styled text (TBC), appending or overwriting existing tags. The timeout parameter, if specified, indicates how long the tag should be displayed (in milliseconds).
function _updateAttr(args)
args =
{
asid : < abstract syntax entity identifier >,
attr : < abstract attribute name >,
val : < new abstract attribute value >,
highlight : true | false
}
Update an attribute of the given entity, specified via its abstract syntax identifier, possibly briefly highlighting the entity to draw attention to the change.